Miniature Current Transformers: The Cornerstone for Sensing in Electrical Systems, The Hidden Engine for Smart Empowerment
Dec, 18 2025
In the intricate network of modern electrical systems—from smart meters and solar inverters to industrial robots—there exists a component that, though tiny, plays an indispensable role: the Miniature Current Transformer (Mini-CT). Hidden within countless devices, it serves as the cornerstone for safe, accurate current measurement and system protection. As digitalization and electrification sweep across the globe, understanding the growing importance of this "unsung hero" is becoming increasingly vital.
I. Core Definition: What is a Miniature Current Transformer?
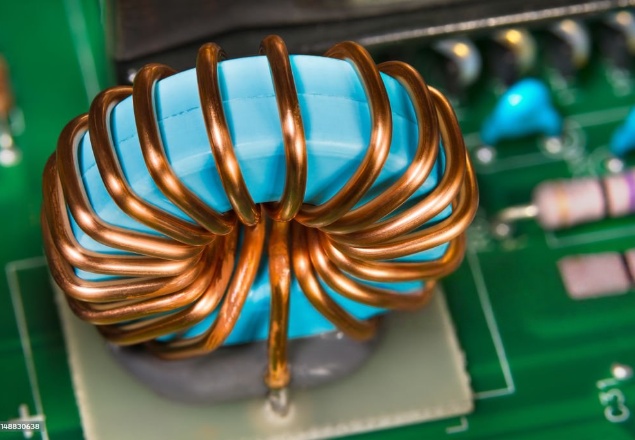
A miniature current transformer represents the miniaturized and integrated evolution of traditional current transformers. Its core mission is based on the principle of electromagnetic induction: to safely and proportionally convert high-current, high-voltage signals from the primary side into low-current signals on the secondary side, while achieving essential electrical isolation.
Unlike bulky industrial-grade counterparts, Mini-CTs are typically no larger than a coin or a fingernail, designed specifically for printed circuit board (PCB) integration or compact spaces. This enables precise current monitoring in devices such as smart meters and IoT sensors.
II. Working Principle: The Ingenious Application of Electromagnetic Induction.
The operational process follows Faraday's Law and can be simplified into four key steps:
Flux Generation: The alternating current being measured (primary side) flows through a conductor (acting as a single-turn coil), generating alternating magnetic flux in a high-efficiency core (e.g., ferrite, nanocrystalline).
Signal Induction: The multi-turn secondary winding around the core induces a proportional alternating current.
Proportional Transformation: The transformation ratio is strictly determined by the turns ratio (e.g., 1000:1 converts 100A to 0.1A).
Signal Output: The secondary current passes through a sampling resistor, converting it into a voltage signal readable by a microprocessor.
Safety Warning: During operation, the secondary side must never be open-circuited, as this can generate dangerously high voltages, posing risks to personnel and equipment.
III. Key Features: Small Size, High Performance.
The Mini-CT is far more than just a "scaled-down" version; it is deeply optimized for modern electronic needs:
High Accuracy and Wide Bandwidth: Accuracy can reach ±0.1%, with frequency response covering from 50Hz to tens of kHz, meeting diverse needs from power frequency metering to switch-mode power supply monitoring.
Excellent Electrical Isolation: Provides isolation voltages up to several thousand volts, building a robust safety barrier.
Low Loss and High Efficiency: Advanced core materials ensure minimal self-power consumption, reducing impact on the measured circuit to the greatest extent.
High Cost-Effectiveness and Easy Integration: Suitable for mass production, offering various packages like PCB mount, through-hole, and clip-on styles, greatly simplifying design.
IV. Core Applications: Empowering Diverse Industries.
Smart Grids and Energy Metering: Acting as the "heart" of smart meters, enabling advanced functions like time-of-use pricing and load monitoring, making them key sensors for grid digitalization.
Industrial Automation: Providing real-time phase current feedback in variable frequency drives (VFDs), servo drives, and robots, enabling overload protection and precise control.
Renewable Energy: Photovoltaic inverters and wind turbine converters rely on them for accurate DC and AC side current sampling to maximize power generation efficiency and grid synchronization.
Consumer Electronics and IoT: Integrated into smart sockets, charging piles, and energy managers, facilitating user-side energy conservation and power usage visualization.
Specialized Fields: Providing stable and reliable electrical parameter monitoring in rail transit, data center UPS systems, and high-end medical equipment.
V. Selection Guide: Quick Reference for Key Parameters.
Selecting the right Mini-CT for your application requires a systematic evaluation of the following parameters:
Consideration Dimension
Key Parameters & Explanation
Electrical Parameters
Rated Current/Turns Ratio: Match the measurement range. Accuracy Class: (0.1, 0.2, 0.5, 1.0). Burden Resistance: Must not exceed the rated value.
Frequency & Safety
Frequency Range: Must cover the operating frequency (power frequency/high frequency). Isolation Voltage: Must be higher than the system's maximum voltage.
Mechanical & Environmental
Mounting Style: PCB, through-hole, clip-on. Operating Temperature/Humidity: Suitable for the application environment.
VI. Future Trends: Moving Towards Smarter, More Integrated Solutions.
The technological forefront is reshaping the future form of Mini-CTs:
Material Innovation: New materials like nanocrystalline alloys are further reducing size and losses while improving accuracy and bandwidth.
Intelligent Integration: "Smart sensor" type CTs with built-in self-diagnostics and digital outputs (e.g., I²C) are emerging, simplifying system design.
Technology Convergence: Coreless technologies like optical current sensing are entering high-end applications, offering near-ideal isolation and interference immunity.
Market Drivers: Emerging fields such as electric vehicle fast charging, energy storage systems, and smart buildings are continuously creating new growth demands.
Conclusion
The miniature current transformer, this precise component hidden deep within circuits, is silently supporting society's electrification and intelligentization with its safety, accuracy, and efficiency. For engineers, decision-makers, and the entire industry, deeply understanding and effectively utilizing this key component is undoubtedly a crucial step in building more reliable, efficient, and intelligent power systems. As technology evolves, its role will shift from "silent measurement" to "active sensing," unlocking even greater value in the future electrical ecosystem.